Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the SQLite NTILE() function to divide a result set into a number of buckets and assign a bucket number to each row.
Introduction to SQLite NTILE() function
SQLite NTILE() function is a window function that divides an ordered result set into a number of buckets by a specified expression and assigns an appropriate bucket number to each row.
The following shows the syntax of the NTILE() function:
NTILE(expression) OVER (
PARTITION BY expression1, expression2,...
ORDER BY expression1 [ASC | DESC]expression2,
)
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax:
expression
The expression can be a literal positive integer or any valid expression that resolves to a positive integer.
The NTILE() function assigns numbers from 1 through the value of the expression to each row. The number of rows in buckets can differ by at most 1. The remainder of the number of rows divided by buckets is allocated to each bucket, starting with bucket 1.
For example, if you have 10 rows and 4 buckets. Each bucket will have 2 rows. The remainder of 10/4 is 2. So the first bucket will have 2 + 1 = 3 rows, the second bucket will also have 3 rows.
The following picture illustrates the idea:
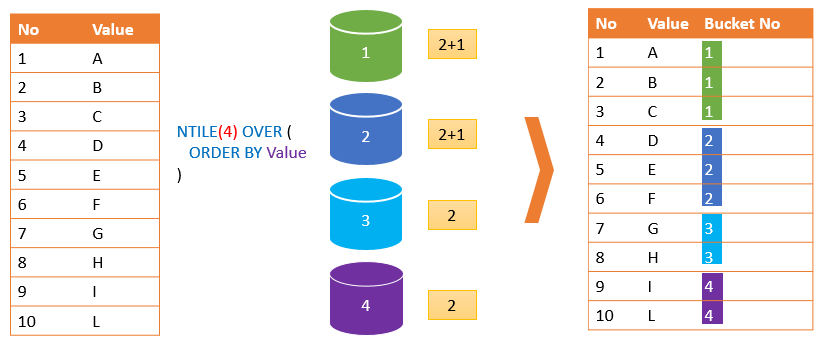
If the value of the expression is greater than the number of rows, then the NTILE() function will fill the number of buckets equal to the number of rows. Hence, the remaining buckets will be empty.
For example, if you have 10 rows and 11 buckets, each row will be assigned a bucket number from 1 to 10. The 11th bucket will have no row.
Notice that you cannot use a subquery or a window function in the expression.
PARTITION BY
The PARTITION BY clause divides the result sets into partitions to which the NTILE function applies.
ORDER BY
The ORDER BY clause specifies the order of rows in each partition to which the NTILE() applies.
SQLite NTILE() function examples
We will use the tracks table from the sample database to demonstrate the NTILE() function:
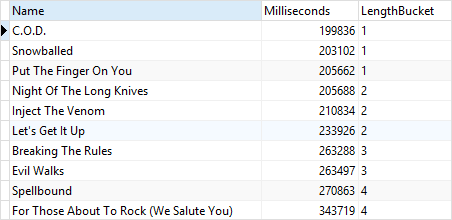
1) Using the NTILE() function with ORDER BY example
The following statement uses the NTILE() function to divide into 4 buckets the values in the Milliseconds column of the tracks table from the album 1:
SELECT
Name,
Milliseconds,
NTILE (4) OVER (
ORDER BY
Milliseconds
) LengthBucket
FROM
tracks
WHERE
AlbumId = 1;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the output:
2) Using the NTILE() function with PARTITION BY clause example
The following statement uses the NTILE() function to divide the tracks of each album into 3 buckets by the values in the Bytes column:
SELECT
AlbumId,
Name,
Milliseconds,
NTILE (3) OVER (
PARTITION BY
AlbumId
ORDER BY
Bytes
) SizeBucket
FROM
tracks;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following picture shows the output:
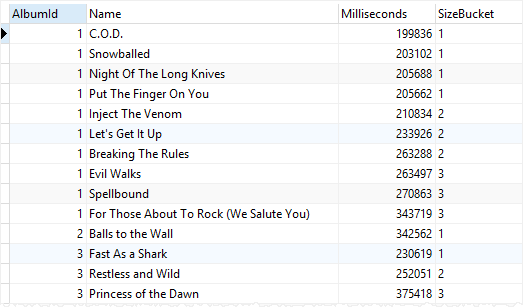
In this example,
- The
PARTITION BYclause distributes the rows into partitions or albums. - The
ORDER BYclause sorts the tracks in each album by their sizes in bytes.
The NTILE() function assigned a bucket number to each track and reset the bucket number for each album.
Summary
- Use the SQLite
NTILE()function to divide a result set into a number of buckets and assign a bucket number to each row.