Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the SQLite LAST_VALUE() function to get the value of the last row in a specified window frame.
Introduction to the LAST_VALUE() function
The LAST_VALUE() is a window function that allows you to obtain the value of the last row in a specified window frame.
Here is the syntax of the LAST_VALUE() function:
LAST_VALUE(expression) OVER (
PARTITION BY expression1, expression2,...
ORDER BY expression1 [ASC | DESC], expression2,..
frame_clause
)Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Let’s examine the syntax in more detail:
expression
It is a valid expression evaluated against the last row in the window frame. The expression must return a single result set. It is not allowed to use a subquery or another window function in the expression.
PARTITION BY
The PARTITION BY clause divides the result set into partitions by one or more criteria to which the LAST_VALUE() function applies. The PARTITION BY clause is optional. If you skip it, the LAST_VALUE() function will treat the whole result set as a single partition.
ORDER BY
The ORDER BY clause sorts the rows in each partition to which the LAST_VALUE() function applies.
frame_clause
The frame_clause defines the subset (or the frame) of the current partition. For more detailed information on the frame clause, check it out the window frame clause tutorial.
SQLite LAST_VALUE() function examples
We’ll use the following tracks table from the sample database for the demonstration purpose:
1) Using the LAST_VALUE() function over the result set example
The following example uses the LAST_VALUE() function to return the track name, the track’s length in minutes, and the longest track of the album id 4:
SELECT
Name,
printf ('%.f minutes', Milliseconds / 1000 / 60) AS Length,
LAST_VALUE (Name) OVER (
ORDER BY
Milliseconds RANGE BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING
AND UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING
) AS LongestTrack
FROM
tracks
WHERE
AlbumId = 4;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Here is the output:
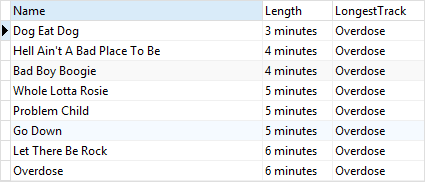
In this example, the ORDER BY clause sorted the tracks from the album id 4 by their lengths and the LAST_VALUE() function selected the last track from the result set which is the longest track.
The following frame clause defines the window frame that starts at the first row and ends at the last row of the partition:
RANGE BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND
UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Note that we used the printf() function to format the length of the track in minutes.
2) Using the LAST_VALUE() over partitions example
The following example shows all tracks from all albums. In addition, it shows the shortest track for each album:
SELECT
AlbumId,
Name,
printf ('%.f minutes', Milliseconds / 1000 / 60) AS Length,
LAST_VALUE (Name) OVER (
PARTITION BY AlbumId
ORDER BY Milliseconds DESC
RANGE BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING
AND UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING
) AS ShortestTrack
FROM
tracks;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following picture displays the partial output:
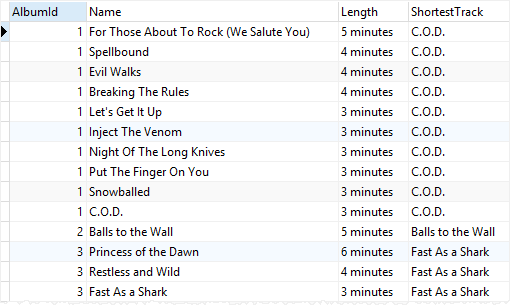
In this example:
- First, the
PARTITION BYclause divided the tracks by album id. - Then, the
ORDER BYclause sorted tracks by their lengths from long to short. - Finally, the
LAST_VALUE()selected the last track in each window frame which is the shortest track in each album.
Summary
- Use the
LAST_VALUE()function to obtain the value of the last row in a specified window frame.