Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use SQLite UPDATE statement to update data of existing rows in the table.
Introduction to SQLite UPDATE statement
To update existing data in a table, you use SQLite UPDATE statement. The following illustrates the syntax of the UPDATE statement:
UPDATE table
SET column_1 = new_value_1,
column_2 = new_value_2
WHERE
search_condition
ORDER column_or_expression
LIMIT row_count OFFSET offset;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax:
- First, specify the table where you want to update after the
UPDATEclause. - Second, set new value for each column of the table in the
SETclause. - Third, specify rows to update using a condition in the
WHEREclause. TheWHEREclause is optional. If you skip it, theUPDATEstatement will update data in all rows of the table. - Finally, use the
ORDER BYandLIMITclauses in theUPDATEstatement to specify the number of rows to update.
Notice that if use a negative value in the LIMIT clause, SQLite assumes that there are no limit and updates all rows that meet the condition in the preceding WHERE clause.
The ORDER BY clause should always goes with the LIMIT clause to specify exactly which rows to be updated. Otherwise, you will never know which row will be actually updated; because without the ORDER BY clause, the order of rows in the table is unspecified.
SQLite UPDATE statement examples
We will use the employees table in the sample database to demonstrate the UPDATE statement.
The following SELECT statement gets partial data from the employees table:
SELECT
employeeid,
firstname,
lastname,
title,
email
FROM
employees;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)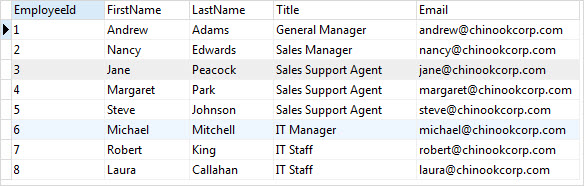
1) Update one column example
Suppose, Jane got married and she wanted to change her last name to her husband’s last name i.e., Smith. In this case, you can update Jane’s last name using the following statement:
UPDATE employees
SET lastname = 'Smith'
WHERE employeeid = 3;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The expression in the WHERE clause makes sure that we update Jane’s record only. We set the lastname column to a literal string 'Smith'.
To verify the UPDATE, you use the following statement:
SELECT
employeeid,
firstname,
lastname,
title,
email
FROM
employees
WHERE
employeeid = 3;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
2) Update multiple columns example
Suppose Park Margaret locates in Toronto and you want to change his address, city, and state information. You can use the UPDATE statement to update multiple columns as follows:
UPDATE employees
SET city = 'Toronto',
state = 'ON',
postalcode = 'M5P 2N7'
WHERE
employeeid = 4;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To verify the UPDATE, you use the following statement:
SELECT
employeeid,
firstname,
lastname,
state,
city,
PostalCode
FROM
employees
WHERE
employeeid = 4;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
3) Update with ORDER BY and LIMIT clauses example
Notice that you need to build SQLite with SQLITE_ENABLE_UPDATE_DELETE_LIMIT option in order to perform UPDATE statement with optional ORDER BY and LIMIT clauses.
Let’s check the email addresses of employees in the employees table:
SELECT
employeeid,
firstname,
lastname,
email
FROM
employees;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)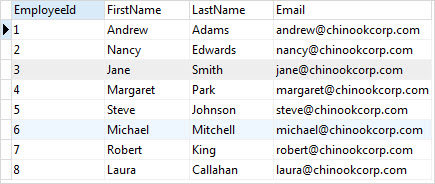
To update one row in the employees table, you use LIMIT 1 clause. To make sure that you update the first row of employees sorted by the first name, you add the ORDER BY firstname clause.
So the following statement updates email of Andrew Adams:
UPDATE employees
SET email = LOWER(
firstname || "." || lastname || "@chinookcorp.com"
)
ORDER BY
firstname
LIMIT 1;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)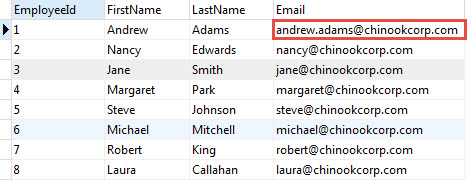
The new email is the combination of the first name, dot (.), last name and the suffix @chinookcorp.com
The LOWER() function converts the email to lower case.
4) Update all rows example
To update all rows in the employees table, you skip the WHERE clause. For example, the following UPDATE statement changes all email addresses of all employees to lowercase:
UPDATE employees
SET email = LOWER(
firstname || "." || lastname || "@chinookcorp.com"
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)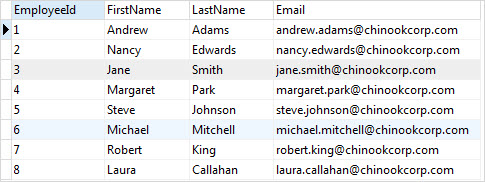
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the SQLite UPDATE statement to update existing data in a table.
References
- https://www.sqlite.org/lang_update.html – SQLite Update statement