Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the SQLite EXCEPT operator to combine result sets of two queries and returns the distinct rows from the first query that are not present in the output of the second query.
Introduction to SQLite EXCEPT operator
SQLite EXCEPT operator compares the result sets of two queries and returns distinct rows from the first query that are not output by the second query.
The following shows the syntax of the EXCEPT operator:
SELECT select_list1
FROM table1
EXCEPT
SELECT select_list2
FROM table2;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)This query must conform to the following rules:
- First, the number of columns in the select lists of both queries must be the same.
- Second, the order of the columns and their types must be comparable.
The following statements create two tables t1 and t2 and insert some data into both tables:
CREATE TABLE t1 (c1 INT);
INSERT INTO
t1 (c1)
VALUES
(1),
(2),
(3);
CREATE TABLE t2 (c2 INT);
INSERT INTO
t2 (c2)
VALUES
(2),
(3),
(4);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The following statement illustrates how to use the EXCEPT operator to compare result sets of two queries:
SELECT c1 FROM t1
EXCEPT
SELECT c2 FROM t2;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Output:
c1
--
1The following picture illustrates the EXCEPT operation:
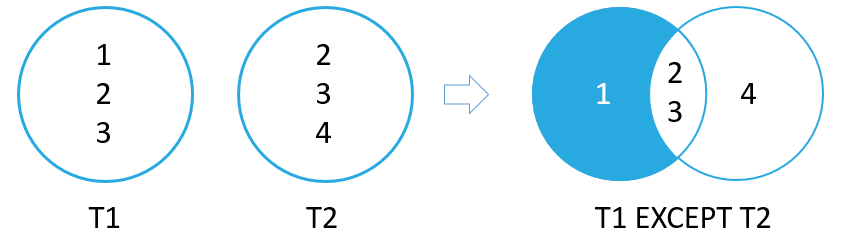
SQLite EXCEPT operator example
First, create new tables books, customers, and orders:
CREATE TABLE books (
book_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
title TEXT,
author TEXT,
genre TEXT,
price REAL
);
CREATE TABLE customers (
customer_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT,
email TEXT
);
CREATE TABLE orders (
order_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
customer_id INTEGER,
book_id INTEGER,
order_date DATE,
FOREIGN KEY (customer_id) REFERENCES customers(customer_id),
FOREIGN KEY (book_id) REFERENCES books(book_id)
);Second, insert rows into these tables:
INSERT INTO books (title, author, genre, price)
VALUES
('To Kill a Mockingbird', 'Harper Lee', 'Fiction', 12.99),
('1984', 'George Orwell', 'Science Fiction', 10.99),
('The Great Gatsby', 'F. Scott Fitzgerald', 'Classic', 9.99),
('Pride and Prejudice', 'Jane Austen', 'Romance', 8.99),
('The Catcher in the Rye', 'J.D. Salinger', 'Fiction', 11.99);
INSERT INTO customers (name, email)
VALUES
('Alice', '[email protected]'),
('Bob', '[email protected]'),
('Charlie', '[email protected]');
INSERT INTO purchases (customer_id, book_id, purchase_date)
VALUES
(1, 1, '2024-04-25'), -- Alice purchased 'To Kill a Mockingbird'
(1, 3, '2024-04-27'), -- Alice purchased 'The Great Gatsby'
(2, 2, '2024-04-26'); -- Bob purchased '1984'Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Third, use the EXCEPT operator to find books that have not had any sales:
SELECT title, author, genre, price
FROM books
EXCEPT
SELECT title, author, genre, price
FROM books
JOIN orders ON books.book_id = orders.book_id;Output:
title author genre price
---------------------- ------------- ------- -----
Pride and Prejudice Jane Austen Romance 8.99
The Catcher in the Rye J.D. Salinger Fiction 11.99Code language: CSS (css)How it works.
- The first query selects all books from the
bookstable. - The second query retrieves books that have orders by joining the
bookstable with theorderstable. - The
EXCEPToperator returns a list of distinct books that have not been ordered by any customer.
Summary
- Use the
EXCEPToperator to combine result sets of two queries and return unique rows from the first query that are not output by the second query.