Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the SQLite SUM function to calculate the sum of all values.
Introduction to SQLite SUM function
The SUM function is an aggregate function that returns the sum the non-NULL values or only the distinct values in a group.
The following expression illustrates the syntax of the SUM function:
SUM([ALL | DISTINCT] expression);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The SUM function uses ALL clause by default. It means that all the input values, whether duplicate or not, are considered when the SUM function performs the calculation.
If you want to calculate the sum of unique values, you have to specify the DISTINCT clause explicitly in the expression.
The result of the SUM function is an integer if all input non-NULL values are integers. If any input value is neither an integer nor a NULL value, the result of the SUM function is a floating-point value.
The result of the SUM function is NULL if and only if all input values are NULL.
In case there is an integer overflow error happens and all input values are NULL or integers, the SUM function throws an integer overflow exception.
SQLite SUM function examples
We will use the tracks table in the sample database for the demonstration.
To get the total length of all tracks in the tracks table, you use the SUM function as the following statement:
SELECT
SUM(milliseconds)
FROM
tracks;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)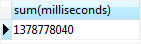
SQLite SUM function with GROUP BY clause
To calculate the total length of each album, you need to use the SUM function with the GROUP BY clause.
First, the GROUP BY clause groups a set of tracks by albums. Then, the SUM function calculates the sum of lengths of tracks per album.
The following statement illustrates the idea:
SELECT
AlbumId,
SUM(milliseconds)
FROM
tracks
GROUP BY
AlbumId;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)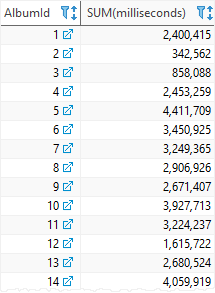
SQLite SUM function and INNER JOIN clause example
To include the album titles in the output, you join the tracks table to the albums table using the INNER JOIN clause as follows:
SELECT
tracks.albumid,
title,
SUM(milliseconds)
FROM
tracks
INNER JOIN albums ON albums.albumid = tracks.albumid
GROUP BY
tracks.albumid,
title;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)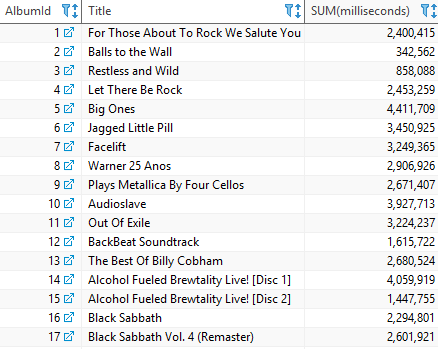
SQLite SUM function and HAVING clause example
You can use the SUM function in the HAVING clause to filter groups based on a specified condition.
For example, the following statement gets all albums whose total lengths are greater than 1,000,000 milliseconds:
SELECT
tracks.albumid AlbumId,
Title,
SUM(milliseconds)
FROM
tracks
INNER JOIN albums ON albums.albumid= tracks.albumid
GROUP BY
tracks.albumid,
title
HAVING
SUM(milliseconds) > 1000000;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
In this tutorial, we have introduced you to the SQLite SUM function that returns the sum of values in a group.