Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the SQLite coalesce() function to handle null values.
Introduction to the SQLite coalesce() function
The coalesce() function accepts two or more arguments and returns the first non-null argument.
Here’s the syntax of the coalesce() function:
coalesce(parameter1,parameter2, …);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)If all the arguments are NULL, the coalesce function returns NULL.
Please note that the coalesce() function is equivalent to the NVL function in Oracle or the IFNULL function in MySQL.
SQLite coalesce() function examples
Let’s take some examples of using the coalesce() function.
1) Basic SQLite coalesce() function examples
The following query uses the coalesce() function to return the first non-null value, which is 10:
SELECT COALESCE(10,20); -- return 10Code language: JavaScript (javascript)The following statement also uses the coalesce() function to return the first non-null argument, which is 20:
SELECT COALESCE(NULL,20,10); -- returns 20Code language: PHP (php)2) Using coalesce() function to substitute NULL
We’ll use the following customers table in the sample database:
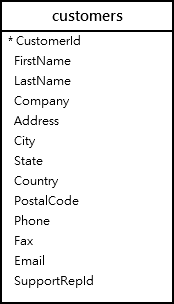
The following query returns the first name, last name, and the company of the customers:
SELECT firstname,
lastname,
company
FROM customers
ORDER BY firstname;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)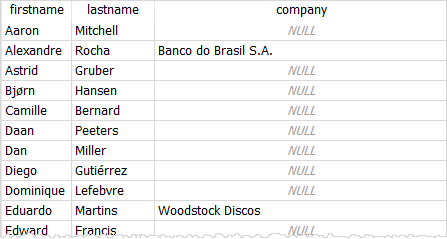
In the customers table, the company information of the customers may be NULL.
But you can use the coalesce() function to replace NULL with another value such as individual. For example:
SELECT firstname,
lastname,
coalesce(company, 'Individual') entity
FROM customers
ORDER BY firstname;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)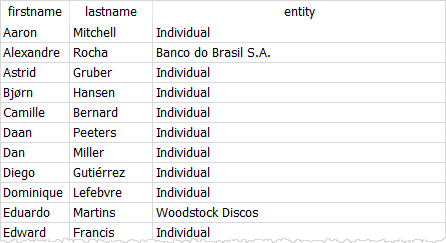
3) Using coalesce() function in expressions
First, create a new table called memberships that stores the program name, net price, and discount.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS memberships (
membership_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
program_name TEXT NOT NULL,
net_price NUMERIC NOT NULL,
discount NUMERIC
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Second, insert some sample data into the memberships table; use the NULL value for the membership that does not have the discount.
INSERT INTO memberships(program_name, net_price, discount)
VALUES('1 Month', 100, null),
('3 Months', 300, 10),
('6 Months', 600, 30);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Third, query data from the memberships table; calculate the amount that members have to pay by subtracting the discount from the net price.
SELECT program_name,
(net_price - discount) AS amount
FROM memberships;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)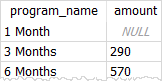
The amount of the 1-month membership is NULL because the discount value is NULL. To avoid this error, you use the coalesce() function as follows:
SELECT program_name,
(net_price - coalesce(discount, 0) ) AS amount
FROM memberships;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)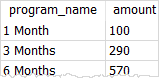
Summary
- Use the
coalesce()function to return the first non-null argument.