Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to remove a table from the database using SQLite DROP TABLE statement.
Introduction to SQLite DROP TABLE statement
To remove a table in a database, you use SQLite DROP TABLE statement. The statement is simple as follows:
DROP TABLE [IF EXISTS] [schema_name.]table_name;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax, you specify the name of the table which you want to remove after the DROP TABLE keywords.
SQLite allows you to drop only one table at a time. To remove multiple tables, you need to issue multiple DROP TABLE statements.
If you remove a non-existing table, SQLite issues an error. If you use IF EXISTS option, then SQLite removes the table only if the table exists, otherwise, it just ignores the statement and does nothing.
If you want to remove a table in a specific database, you use the [schema_name.] explicitly.
In case the table has dependent objects such as triggers and indexes, the DROP TABLE statement also removes all the dependent objects.
The DROP TABLE statement performs an implicit DELETE statement before dropping the table. However, the DROP TABLE statement removes the triggers associated with the table before performing the implicit DELETE statement, therefore, the delete triggers will not fire.
If the foreign key constraints enabled and you perform the DROP TABLE statement, before SQLite performs the implicit DELETE statement, it carries the foreign key constraints check. If a foreign key constraint violation occurs, SQLite issues an error message and will not drop the table.
Notice that the DROP TABLE statement deletes the table from the database and the file on disk completely. You will not be able to undo or recover from this action. Therefore, you should perform the DROP TABLE statement with extra caution.
SQLite DROP TABLE statement examples
For the demonstration purpose, we will create two tables: people and addresses. Each person has one address. And one address can be shared by multiple people.
First, create the tables:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS people (
person_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
first_name TEXT,
last_name TEXT,
address_id INTEGER,
FOREIGN KEY (address_id)
REFERENCES addresses (address_id)
);
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS addresses (
address_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
house_no TEXT,
street TEXT,
city TEXT,
postal_code TEXT,
country TEXT
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)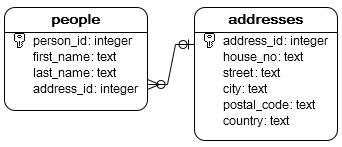
Second, insert an address and a person into the addresses and people tables.
INSERT INTO addresses ( house_no, street, city, postal_code, country )
VALUES ( '3960', 'North 1st Street', 'San Jose ', '95134', 'USA ' );
INSERT INTO people ( first_name, last_name, address_id )
VALUES ('John', 'Doe', 1);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Third, use the DROP TABLE statement to remove the addresses table.
DROP TABLE addresses;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)SQLite issued an error message:
constraint failedCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Because this action violates the foreign key constraint.
To remove the addresses table, you have to:
- Disable foreign key constraints.
- Drop the
addressestable. - Update the
address_idin thepeopletable toNULLvalues. - Enable the foreign key constraints.
See the following statements:
PRAGMA foreign_keys = OFF;
DROP TABLE addresses;
UPDATE people
SET address_id = NULL;
PRAGMA foreign_keys = ON;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The addresses table is removed and values of the address_id column are updated to NULL values.
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use SQLite DROP TABLE statement to remove the table completely from a database.