Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use SQLite INSERT statement to insert new rows into a table.
To insert data into a table, you use the INSERT statement. SQLite provides various forms of the INSERT statements that allow you to insert a single row, multiple rows, and default values into a table.
In addition, you can insert a row into a table using data provided by a SELECT statement.
SQLite INSERT – inserting a single row into a table
To insert a single row into a table, you use the following form of the INSERT statement:
INSERT INTO table (column1,column2 ,..)
VALUES( value1, value2 ,...);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Let’s examine the INSERT statement in more detail:
- First, specify the name of the table to which you want to insert data after the
INSERT INTOkeywords. - Second, add a comma-separated list of columns after the table name. The column list is optional. However, it is a good practice to include the column list after the table name.
- Third, add a comma-separated list of values after the
VALUESkeyword. If you omit the column list, you have to specify values for all columns in the value list. The number of values in the value list must be the same as the number of columns in the column list.
We will use the artists table in the sample database for the demonstration.

The following statement insert a new row into the artists table:
INSERT INTO artists (name)
VALUES('Bud Powell');Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Because the ArtistId column is an auto-increment column, you can ignore it in the statement. SQLite automatically geneate a sequential integer number to insert into the ArtistId column.
You can verify the insert operation by using the following SELECT statement:
SELECT
ArtistId,
Name
FROM
Artists
ORDER BY
ArtistId DESC
LIMIT 1;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
As you see, we have a new row in the artists table.
SQLite INSERT – Inserting multiple rows into a table
To insert multiple rows into a table, you use the following form of the INSERT statement:
INSERT INTO table1 (column1,column2 ,..)
VALUES
(value1,value2 ,...),
(value1,value2 ,...),
...
(value1,value2 ,...);
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Each value list following the VALUES clause is a row that will be inserted into the table.
The following example inserts three rows into the artists table:
INSERT INTO artists (name)
VALUES
("Buddy Rich"),
("Candido"),
("Charlie Byrd");Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)SQLite issued a message:
Row Affected: 3You can verify the result using the following statement:
SELECT
ArtistId,
Name
FROM
artists
ORDER BY
ArtistId DESC
LIMIT 3;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)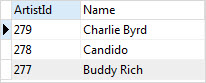
SQLite INSERT – Inserting default values
When you create a new table using the CREATE TABLE statement, you can specify default values for columns, or a NULL if a default value is not specified.
The third form of the INSERT statement is INSERT DEFAULT VALUES, which inserts a new row into a table using the default values specified in the column definition or NULL if the default value is not available and the column does not have a NOT NULL constraint.
For example, the following statement inserts a new row into the artists table using INSERT DEFAULT VALUES:
INSERT INTO artists DEFAULT VALUES;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To verify the insert, you use the following statement:
SELECT
ArtistId,
Name
FROM
artists
ORDER BY
ArtistId DESC;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)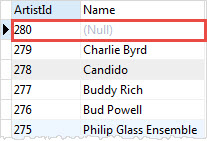
The default value of the ArtistId column is the next sequential integer . However, the name column does not have any default value, therefore, the INSERT DEFAULT VALUES statement inserts NULL into it.
SQLite INSERT – Inserting new rows with data provided by a SELECT statement
Suppose you want to backup the artists table, you can follow these steps:
First, create a new table named artists_backup as follows:
CREATE TABLE artists_backup(
ArtistId INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
Name NVARCHAR
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To insert data into the artists_backup table with the data from the artists table, you use the INSERT INTO SELECT statement as follows:
INSERT INTO artists_backup
SELECT ArtistId, Name
FROM artists;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)If you query data from the artists_backup table, you will see all data in the artists table.
SELECT * FROM artists_backup;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)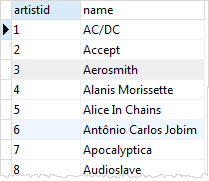
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use various forms of SQLite INSERT statement that insert new rows into a table.
References
- https://www.sqlite.org/lang_insert.html – SQLite INSERT statement